JetBlue (JBLU) Historical Market Capitalization (2020-2024)
5 JetBlue (JBLU) Financial Analysis
JetBlue Airways occupies a competitive space between legacy carriers and ultra-low-cost operators. Analyzing its financial statements is crucial for understanding the strategic challenges and opportunities for airlines with this hybrid model. This section provides a time-series analysis of JetBlue’s key financial metrics, tracing its performance against the backdrop of an evolving industry.
5.1 Market Capitalization
JetBlue’s market capitalization trajectory from 2020 to 2024 reflects the broader industry’s volatility and recovery. The initial sharp decline in early 2020 corresponds with the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic, which severely impacted air travel demand. However, unlike some competitors, JetBlue’s market cap did not recover to pre-pandemic levels by 2024, indicating ongoing challenges in regaining investor confidence amid competitive pressures and operational hurdles.
5.2 Income Statement Overview
5.2.1 Profitability Analysis
JetBlue’s path to profitability has been significantly more challenging than that of its larger peers. While revenue has recovered, consistent bottom-line performance remains elusive.
JetBlue (JBLU) Quarterly Revenue and Net Income (2020-2024)
5.3 Margin Analysis
JetBlue’s recovery trajectory has been fraught with volatility. After a brief return to a small operating and net profit in 2022, the airline slipped back into losses in 2023 and continued to post a net loss in 2024. This persistent margin weakness suggests structural cost pressures, potentially from an uncompetitive labor cost structure or an inefficient route network that faces intense competition from both legacy carriers on premium routes and ultra-low-cost carriers on leisure routes, leaving JetBlue caught in the middle.
JetBlue (JBLU) Quarterly Operating and Net Margins (2020-2024)
5.4 Balance Sheet Health and Leverage
JetBlue’s struggle with profitability is reflected in its deteriorating balance sheet health, marked by rising debt levels.
JetBlue (JBLU) Quarterly Total Assets, Debt and Equity (2020-2024)
5.4.1 Debt-to-Equity Ratio Trend
JetBlue’s financial stability has weakened considerably over the five-year period. While the Net Debt to Equity ratio briefly improved in 2021, it has since escalated dramatically, reaching 5x by the end of 2024. This trend is a direct result of equity erosion from persistent net losses and an increase in net debt to fund operations and investments. Such high leverage poses a significant financial risk and constrains the company’s strategic flexibility.
JetBlue (JBLU) Quarterly Debt-to-Equity Ratio (2020-2024)
5.5 Cash Flow Qjbluity and Sustainability
JetBlue’s cash flow statement further highlights its operational challenges, showing a disconnect between reported earnings and actjblu cash generation.
The pattern is concerning: in years with net losses (2020, 2021, 2023, 2024), cash from operations was also negative, and often worse than the reported loss. This indicates that non-cash charges like depreciation were not sufficient to offset cash drains from operations.
JetBlue (JBLU) Quarterly Net Income and Cash from Operating Activities (2020-2024)
5.5.1 Free Cash Flow Trend
Furthermore, JetBlue’s free cash flow has been consistently and deeply negative over the periods. This inability to generate positive free cash flow underscores a critical lack of financial flexibility and a dependency on external financing to fund its capital expenditures.
JetBlue (JBLU) Quarterly Free Cash Flow (2020-2024)
5.6 Efficiency and Performance Ratios
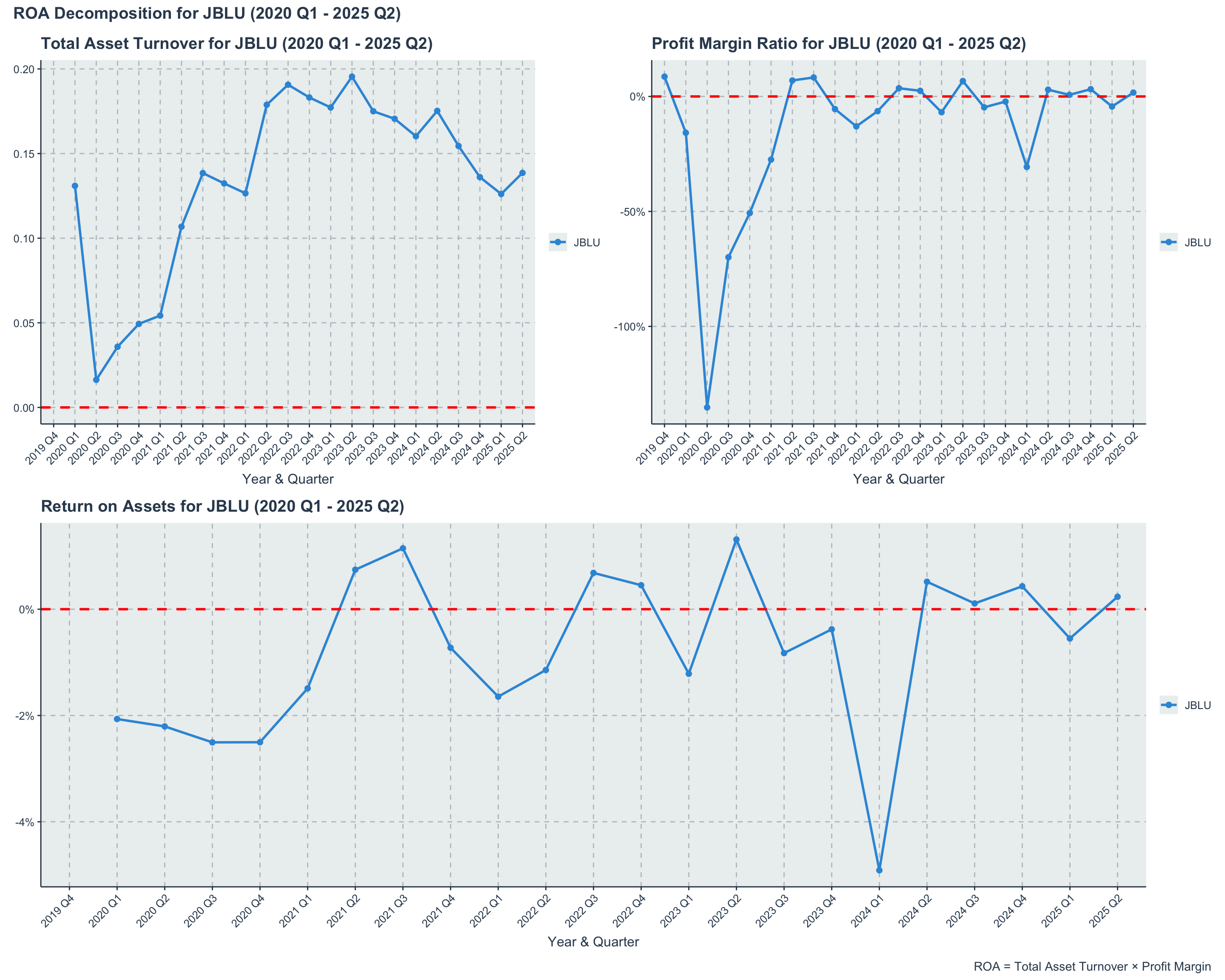
JBLU’s Return on Assets (ROA) has been highly volatile from 2020 to 2024, reflecting the airline’s struggle to generate consistent profits amid fluctuating demand and operational challenges. The ROA dipped into negative territory during the peak pandemic years, with only brief recoveries in between. This inconsistency highlights the difficulties JetBlue faces in efficiently utilizing its asset base to generate earnings.
JetBlue (JBLU) Quarterly Return on Assets (ROA) (2020-2024)
The decomposition of ROA into Total Asset Turnover and Profit Margin provides insights into the drivers behind JetBlue’s asset efficiency. The airline’s low and fluctuating profit margins have been a significant drag on ROA, despite relatively stable asset turnover ratios. This indicates that while JetBlue can generate revenue from its assets, its ability to convert that revenue into profit remains a critical challenge.
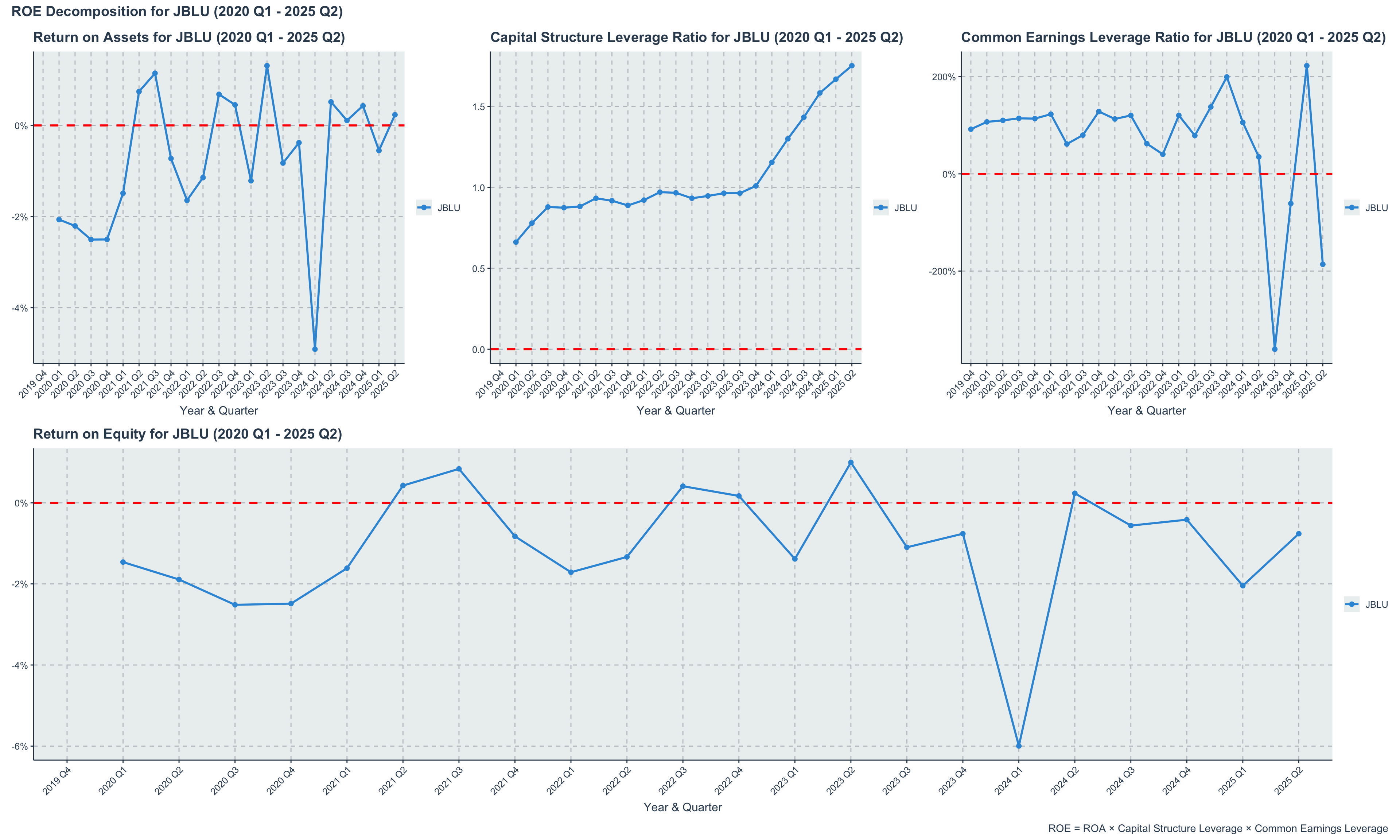
JBLU’s Return on Equity (ROE) has mirrored its ROA trends, with significant fluctuations and periods of negative returns. The airline’s ROE has been particularly affected by its equity erosion due to sustained losses, leading to a challenging environment for shareholders. The negative ROE in several quarters underscores the difficulties JetBlue faces in delivering value to its equity investors.
JetBlue (JBLU) Quarterly Return on Equity (ROE) (2020-2024)
The decomposition of ROE into its constituent components reveals the multifaceted challenges JetBlue faces in delivering shareholder value. The airline’s low ROA, combined with high leverage ratios, has amplified the negative impact on ROE. This analysis underscores the critical need for JetBlue to improve its operational efficiency and profitability while managing its capital structure prudently to enhance returns for equity investors.
5.7 Summary
In summary, JetBlue’s financial analysis from 2020 to 2024 reveals a company grappling with the dual challenges of recovering from a severe industry downturn while trying to establish a sustainable and profitable business model. The airline’s inability to consistently generate profits, coupled with a deteriorating balance sheet and negative cash flows, raises significant concerns about its long-term viability without substantial strategic changes. JetBlue’s hybrid model, while offering some competitive advantages, appears to be a liability in a market increasingly polarized between low-cost and full-service carriers. Addressing these financial and operational challenges will be critical for JetBlue to regain its footing in the competitive U.S. airline landscape.